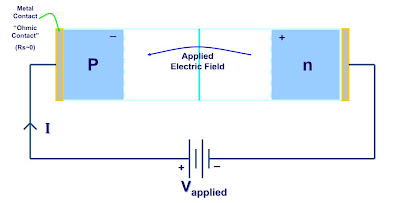
The Biased PN Junction

The pn junction is considered biased when an external voltage is applied. There are two types of biasing: Forward bias and Reverse bias.

Forward Bias (V(applied) > 0) : In forward bias the depletion region shrinks slightly in width. With this shrinking the energy required for charge carriers to cross the depletion region decreases exponentially. Therefore, as the applied voltage increases, current starts to flow across the junction. The barrier potential of the diode is the voltage at which appreciable current starts to flow through the diode. The barrier potential varies for different materials.
Reverse Bias (V(applied) < 0) : Reverse Bias: Under reverse bias the depletion region widens. This causes the electric field produced by the ions to cancel out the applied reverse bias voltage. A small leakage current, Is (saturation current) flows under reverse bias conditions.This saturation current is made up of electron-hole pairs being produced in the depletion region. Saturation current is sometimes referred to as scale current because of it’s relationship to junction temperature.